Class 11th "CHEMICAL BONDINGS AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE"
• General Characteristics of ionic Compounds :
(i) Physical State: They generally exist as crystalline solids, known as crystal lattice. Ionic compounds do not exist as single molecules like other gaseous molecules e.g., H2 , N2 , 02 , Cl2 etc.
(ii) Melting and boiling points: Since ionic compounds contain high interionic force between them, they generally have high melting and boiling points.
(i) Physical State: They generally exist as crystalline solids, known as crystal lattice. Ionic compounds do not exist as single molecules like other gaseous molecules e.g., H2 , N2 , 02 , Cl2 etc.
(ii) Melting and boiling points: Since ionic compounds contain high interionic force between them, they generally have high melting and boiling points.
(iii) Solubility: They are soluble in polar solvents such as water but do not dissolve in organic solvents like benzene, CCl4etc.
(iv) Electrical conductivity: In solid state they are poor conductors of electricity but in molten state or when dissolved in water, they conduct electricity.
(v) Ionic reactions: Ionic compounds produce ions in the solution which gives very fast reaction with oppositely charged ions.
For example,
When the bond is formed between two or more atoms by mutual contribution and sharing of electrons, it is known as covalent bond.
If the combining atoms are same the covalent molecule is known as homoatomic. If they are different, they are known as heteroatomic molecule.

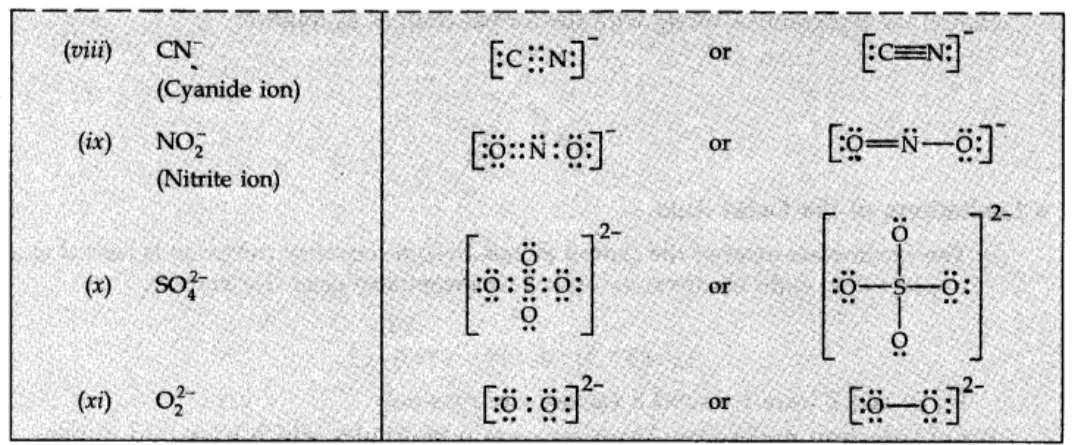
• Lewis Representation of Simple Molecules (the Lewis Structures)
The Lewis dot Structure can be written through the following steps:
(i) Calculate the total number of valence electrons of the combining atoms.
(ii) Each anion means addition of one electron and each cation means removal of one electron. This gives the total number of electrons to be distributed.
(iii) By knowing the chemical symbols of the combining atoms.
(iv) After placing shared pairs of electrons for single bond, the remaining electrons may account for either multiple bonds or as lone pairs. It is to be noted that octet of each atom should be completed.
• Formal Charge :
In polyatomic ions, the net charge is the charge on the ion as a whole and not by particular atom. However, charges can be assigned to individual atoms or ions. These are called formal charges.
It can be expressed as
Thank you !





Comments
Post a Comment