Class 12th "Solutions"
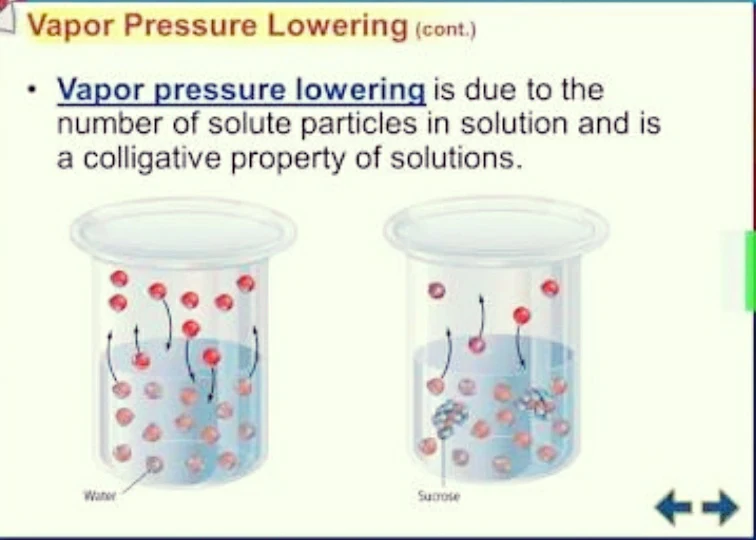
1. Vapour Pressure Lowering : when we adding a vapourised solute in the normal solvent there after changed in vapour pressure is called lowering of vapour pressure.
If any of pure solvent vapour pressure is p° and vapour pressure of solution is p,
Than, lowering of vapour pressure = p°-p
And relative lowering of vapour pressure = p°-p/p°
[A] Measurement of Relative Lowering of Vapour Pressure : for the measurement the Ostward and Walker's dynamic method is most important method to measurement.
[B] Determination of molecular mass of a solute from Relative Lowering of Vapour Pressure : The formula of the calculating the molecular mass of solute as
Where, M' = molecular weight of solute.
w = molar mass of solute.
W = molar mass of solvent.
M = molecular weight of solvent.
• Elevation of Boiling Point :
• Boiling point : it is the temperature that the substances that the vapour pressure are equavalent to the atmospheric pressure is called boiling point.
Example : boiling Point of water is 373K (100°C) e.g. it mean that the vapour pressure of pure water is equavalent to atmospheric pressure at 373K .
[A] Elevation of Boiling Point : Cause of increasing the boiling point when Solute mixed in solvent.
[B] Calculate the Elevation of Boiling Point : The formula is given below
• Depression of Freezing Point : The difference in temperature between a solution freezing point and the freezing point of it's pure solvent.
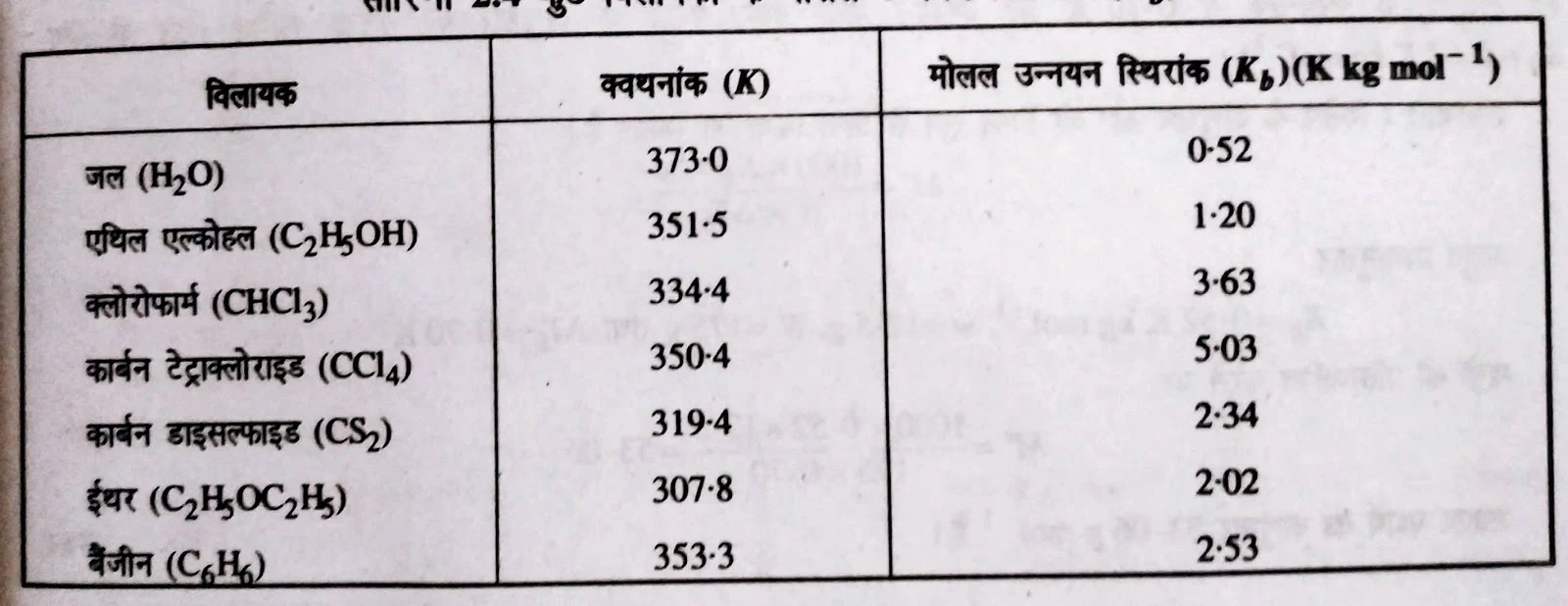
Some Molal Depression Constant of Solvents(Kf) :
[A] Determination of Molecular Mass of the Solute :
Where, Kf = Molal depression Constant.
∆Tf = Freezing point of solvent.
w = molar mass of solute.
W = molar mass of solvent.
M' = molecular weight of solute.
Thank you !















Comments
Post a Comment